CDP vs DMP: Key Differences You Need to Know

Data is an integral part of all aspects of digital marketing. Companies across industries rely on different technical solutions to collect data and turn it into actionable insights. Two of the most popular data management options are data management platforms (DMP) and customer data platforms (CDP).
While both platforms allow you to store and manage data, there are some fundamental differences between the two. In this CDP vs DMP comparison, we’ll analyze the key differences between the two platforms to see which is more useful to your business.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
- What is a DMP?
- Examples of DMPs
- What is a CDP?
- CDP vs DMP: what are the differences?
- CDP vs DMP: which is right for your business?
What is a DMP?
Data management platforms are software solutions designed to collect and manage anonymous user data. DMPs connect to 3rd-party data sets to access massive amounts of information about digital users across the world. The data sets are divided into different categories that represent a particular characteristic of the users. For example, a category based on demographics such as age group. Or a category for users who are interested in traveling.
Examples of DMPs
There are plenty of DMP solutions available to organizations today. Here are a few examples of some popular data management platforms:
Lotame
Lotame is a comprehensive DMP solution that allows organizations to combine data from any source to build the perfect audience segment. The platform comes connected to a data exchange featuring thousands of audience segments built from billions of cookies around the world.
OnAudience
OnAudience helps improve the efficiency of advertising campaigns by allowing you to create detailed customer segments based on the data collected from online and offline sources. The platform provides access to a massive database of over 27 billion user profiles.
What is a CDP?
Customer data platforms are software solutions designed to provide a centralized place to collect, manage and distribute all your customer data. The interest in CDPs has risen as marketers need a more effective way to leverage their data to improve customer engagement.
CDPs can gather data from a variety of data sources including customer relationship management systems (CRM), websites, apps, and more. You can even connect a DMP to your customer data platform to aggregate data in a single place. Once the data is in the system you can manage it in a variety of ways. This could be adding tags to customers or using segmentation to create new audience groups.
CDP vs DMP: what are the differences?
Both CDP and DMPs allow you to collect and manage customer data but they do so in very different ways. Let’s take a closer look at the key differences between the two platforms:
Personal vs anonymous data
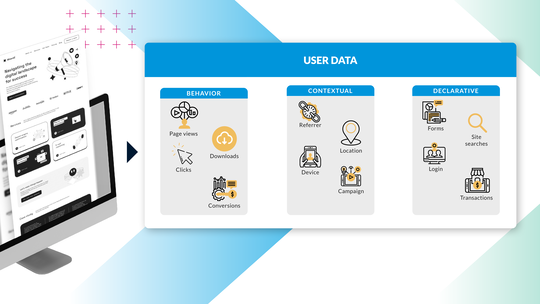
The biggest difference between CDPs and DMPs is the type of data the solutions store. DMPs do not collect any first-party data or personally identifiable information (PII). The software only gathers and stores non-identifying information such as IP addresses, cookies, browser, and device type.
CDPs on the other hand collect and store all forms of first, second, and third-party data. This includes both anonymous data and personally identifiable data such as names, emails, addresses, and phone numbers. CDPs combine these various forms of data to create a unified customer profile for each individual. Profiles are updated in real-time as new pieces of data enter the system.
Use cases
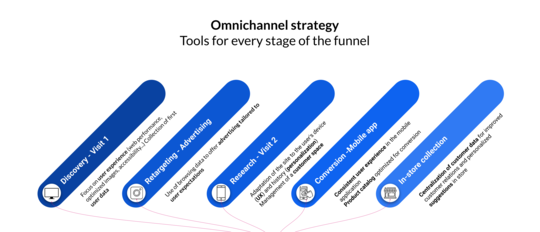
CDPs and DMPs both deal in data but vary drastically in their functionality and use cases. DMPs are primarily used for paid advertising. They improve media buying efficiency by giving marketers the ability to target their audience in more detail. You can use the data from the DMP to build programmatic ad campaigns and extend your targeting by creating lookalike audiences.
CDPs are built to support a wider range of marketing applications. The software provides flexible compatibility with the other systems in your martech stack, allowing you to easily syndicate data to other platforms. Marketing teams can take this data to enhance the customer experience by adding personalized messaging that is highly relevant to each individual.
Data storage structure
CDPs and DMPs also differ in how they store and retain data. CDPs store data in a single place. Doing so makes the platform faster and more flexible as it can analyze all the data at the same time. DMPs use two different data stores for handling data.
CDPs typically have long retention periods to enable marketers to build detailed profiles over a customer’s lifetime. DMPs typically retain data for a much shorter period as their primary use case is for ad targeting for current marketing campaigns.
CDP vs DMP: which is right for your business?
By now we can see that there are some clear differences between CDPs and DMPs. Whether either of these platforms can provide value to your business depends on your particular needs. Advertisers, agencies, and other businesses that want to improve the efficiency of their advertising campaigns can benefit from a DMP. Companies that seek to understand their audience better while improving the customer experience across touchpoints can benefit from a CDP.
For more information about how a customer data platform can maximize the value of your data, check out our jCustomer CDP. The platform is part of the robust Jahia Digital Experience Platform (DXP) and provides users a streamlined interface for managing customer profiles and creating one-of-a-kind experiences at scale.